An engine operates by combining air and fuel in a cylinder. When compressed and ignited by a spark, this mixture creates a mini explosion, driving a piston down that then turns the crankshaft. This creates rotational energy, turning the wheels of your car. By adjusting the sequence of intake, compression, ignition and exhaust strokes, the engine’s efficiency and power output are controlled. Additionally, a timing belt guarantees synchronization between the rotation of the crankshaft and camshaft. As you explore further, you’ll understand more about the unique characteristics of various engine types and how they convert energy into motion.
Key Takeaways
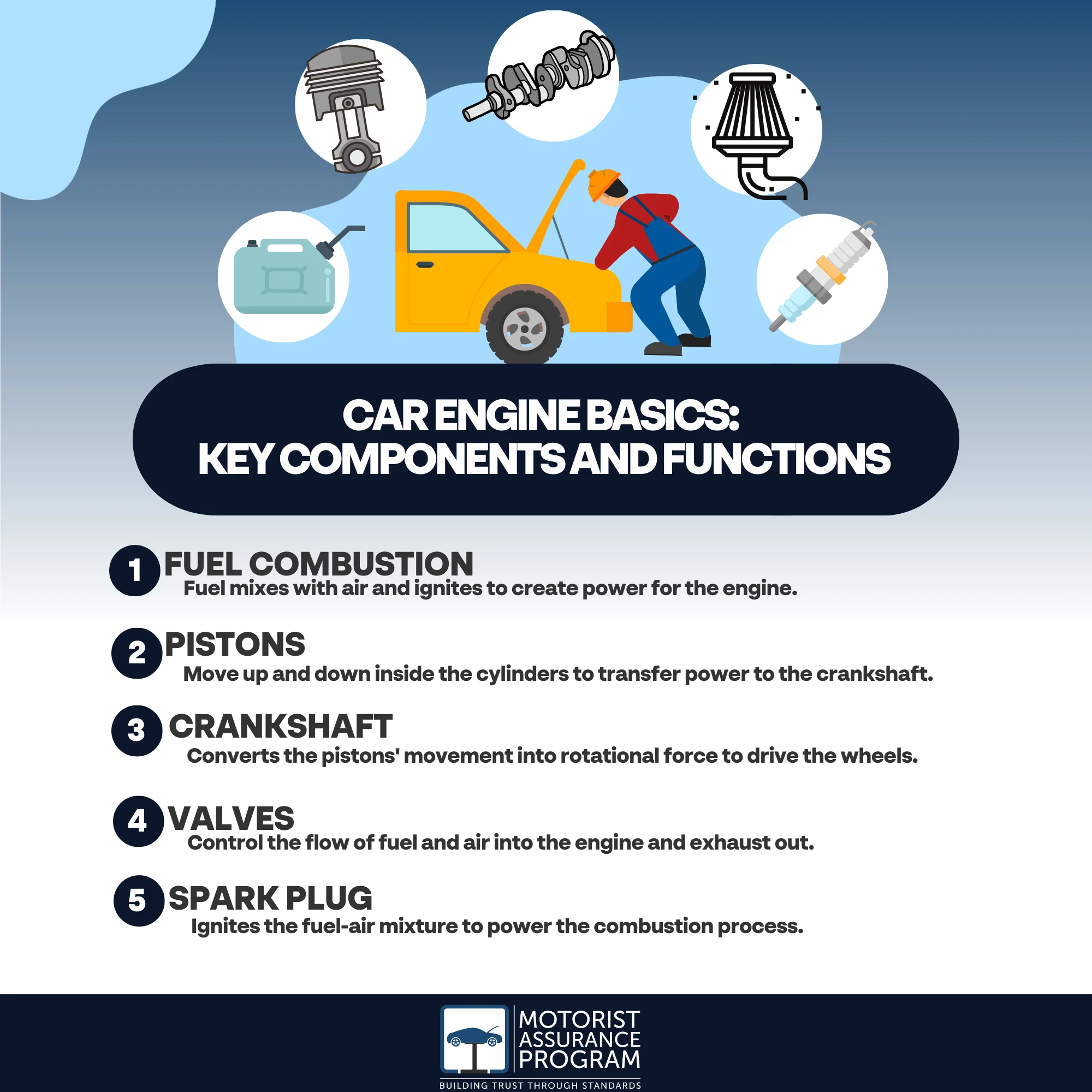
- An engine works by combusting a mixture of air and fuel in a cylinder, creating power to move the car.
- Key engine components include the cylinder, piston, crankshaft, camshaft, and timing belt, each playing a crucial role in engine operation.
- This combustion process, initiated by a spark, pushes a piston down, which in turn rotates the crankshaft, converting chemical energy into mechanical energy.
- The crankshaft’s rotation is coordinated with the camshaft via the timing belt, ensuring accurate opening and closing of the engine’s valves.
- The engine’s power is then adjusted by the transmission before it reaches the driveshaft, which, aided by the differential, transfers power to the wheels, moving the vehicle.
Where Engine Power Comes From
Inside the heart of your car lies the engine, a complex piece of machinery that generates the power needed to move your vehicle. This power is generated through a process that’s more intricate than you might imagine.
So, how does a car engine work step by step?
Let’s break it down. Your car engine operates on the basic principle of internal combustion – air and fuel ignite inside the engine, creating a small explosion that pushes the pistons down. This motion is then converted into rotational energy by the crankshaft, which powers your wheels.
First, the car engine takes in air through the intake valve during the intake stroke. Simultaneously, fuel is injected into the cylinder. This air-fuel mixture is compressed during the compression stroke, and a spark from the spark plug ignites it.
This combustion pushes the piston down, turning the crankshaft. Finally, the exhaust stroke expels the leftover gases out through the exhaust valve.
Understanding how an engine works not only makes you a more informed driver but can also help you diagnose potential problems.
Stay tuned for more insights on car engine mechanics.
The Different Types of Engines
Diving into the world of engines, you’ll find there are several different types, each with its own unique design and operation method.
Let’s explore some of the most common car engines to help you understand how does a car engine work.
First up, you’ve got the Internal Combustion Engine (ICE), the most common type of engine in cars today. It operates by burning fuel inside the engine itself, hence ‘internal combustion’, and this process moves the car.
Next, you’ll encounter the Diesel Engine, named after its inventor Rudolf Diesel. It’s similar to an ICE but uses compressed hot air to ignite the fuel, offering more fuel efficiency.
The Rotary Engine, or Wankel engine, is a fascinating piece of engineering. Instead of using reciprocating pistons like most engines, it utilizes a rotor to convert pressure into a rotating motion.
Lastly, you’ve got the Electric Engine, found in electric vehicles (EVs). These engines use electricity stored in batteries to power an electric motor, producing zero emissions.
Key Engine Parts: What They Do and Why They Matter
Ever wonder about the key components that make your car’s engine run smoothly? Let’s explore the nitty-gritty of how an engine works step by step.
Firstly, you’ve got the cylinder, the engine’s core. It’s fundamentally the power factory where gasoline is transformed into motion.
Then, there’s the piston, moving up and down within the cylinder. As you turn the ignition key, a spark plug ignites the air-fuel mixture in the cylinder, causing an explosion that forces the piston down.
Next, let’s talk about the crankshaft. This part converts the piston’s up-and-down motion into a rotational one that your car’s wheels can use. It’s an essential component in how the engine of a car works.
The camshaft, on the other hand, opens and closes the engine’s intake and exhaust valves, guaranteeing the correct timing for the air-fuel mixture and exhaust gases.
Lastly, there’s the timing belt. This guarantees that the crankshaft and camshaft rotate in sync, critical for the engine’s operation.
Understanding how a car engine works in simple terms can be complex, but once you grasp these key parts, you’re well on your way to becoming an engine expert.
How Engines Turn Energy into Motion: From Power to the Wheels
Often, you may find yourself wondering how the energy created in your car’s engine transforms into motion. Well, it’s a detailed process where fuel’s chemical energy gets converted into mechanical energy.
So, how does an engine work in a car?
Firstly, in the combustion chamber, the fuel-air mix is ignited, causing an explosion. This explosion pushes a piston down, transforming chemical energy into mechanical energy. The piston, connected to a crankshaft, rotates and converts the up-and-down movement into a rotational one.
Now, let’s visualize this with a how does a car engine work diagram. The rotating crankshaft is connected to the transmission, which adjusts the engine’s speed and torque. The transmission, in turn, sends this controlled power to the driveshaft, which reaches the differential.
Here, the power gets split equally between the wheels, causing them to move.
It’s fascinating, isn’t it? This intricate dance of mechanical parts turns fuel into motion, propelling your car forward. Indeed, the process shows the genius of engineering, where power seamlessly flows from the engine to the wheels.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Materials Are Typically Used in Engine Construction?
Engines are typically made from sturdy materials. You’ll find cast iron, aluminum alloys, and steel in most. Cast iron’s used for blocks, while aluminum’s great for reducing weight. Steel’s often found in components like camshafts.
How Often Should an Engine Be Serviced for Optimal Performance?
You should service your engine every 3,000 to 5,000 miles, depending on your vehicle’s make and model. Regular servicing guarantees peak performance, prolongs your engine’s life, and helps prevent costly breakdowns. Don’t neglect this essential maintenance!
What Are Some Common Signs of Engine Problems to Watch Out For?
You’ll notice engine problems if your car’s performance drops, it’s consuming more fuel, there’s smoke from the exhaust, or if the “check engine” light’s on. Strange noises or leaks also indicate possible engine issues.
How Does Engine Size Relate to the Power Output of a Vehicle?
Engine size impacts power output. Larger engines have more cylinders, allowing for more combustion. You’ll get greater power, but also use more fuel. Conversely, smaller engines use less fuel, but generate less power.
What Impact Does Regular Engine Maintenance Have on Fuel Efficiency?
Regular engine maintenance drastically boosts your fuel efficiency. It’s like giving your car a health checkup, ensuring everything’s running smoothly. Neglect it, and you’ll notice your car guzzling more gas than usual. So, don’t skimp on servicing.
Conclusion
So, now you’ve had a peek under the hood! You’ve journeyed from the spark plug’s tiny explosion to the power at your wheels. You’re no longer in the dark ages, just turning a key and hoping for the best. You now understand the magic that happens each time you ignite your engine. It’s more than just mechanics, it’s a symphony of parts working together. Keep exploring, and who knows – maybe one day you’ll build your own engine!


